Showing 7–12 of 21 results
-
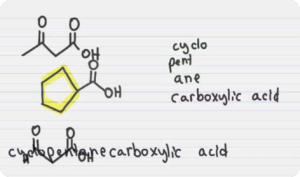
Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives (Digital Notes)
$200.00 Add to cartCarboxylic Acid is an organic compound containing a carboxyl functional group. They occur widely in nature and are also synthetically manufactured by humans. Upon deprotonation, carboxylic acids yield a carboxylate anion with the general formula R-COO–, which can form a variety of useful salts such as soaps.
-
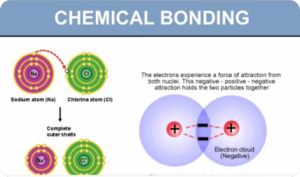
Chemical Bonding (Digital Notes)
$300.00 Add to cartChemical bonding is the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world.
-

Chemical Energetics (Digital Notes)
$250.00 Add to cartThe study of chemical energetics deals with the energy changes during a chemical reaction. During chemical reactions, energy is either released or absorbed. Chemical energetics tells us whether a chemical reaction can take place spontaneously or not and about the feasibility of a reaction.
-
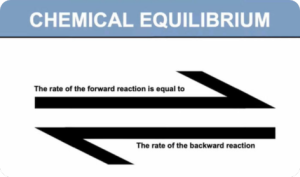
Chemical Equilibria (Digital Notes)
$100.00 Add to cartIn a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both the reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time, so that there is no observable change in the properties of the system. This state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction.
-
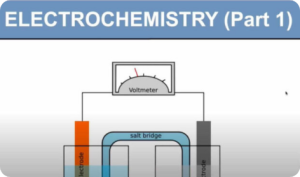
Electrochemical Cell (Digital Notes)
$150.00 Add to cartAn electrochemical cell is a device that can generate electrical energy from the chemical reactions occurring in it, or use the electrical energy supplied to it to facilitate chemical reactions in it.
-
Electrolysis (Digital Notes)
Read moreElectrolysis is a process that involves the use of an electric current to drive a chemical reaction. It is a fundamental process in chemistry and is used in a wide range of applications, including the production of metals, the purification of chemicals, and the generation of electricity.