Showing 13–18 of 21 results
-
Gibbs Free Energy (Digital Notes)
Read moreGibbs free energy, denoted G, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. The change in free energy, ΔG, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system. ΔG can predict the direction of the chemical reaction under two conditions: 1. constant temperature and 2. constant pressure.
-
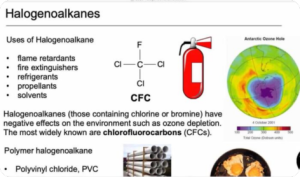
Halogen Derivatives (Digital Notes)
$150.00 Add to cartThe term “halogen derivatives” refer to the organic compounds of halogens which usually contain covalently-bonded halogens. The electronegativity of elements plays a crucial role in deciding which get to bond with halogens and which don’t. The similarity in electronegativity values of H and C render the latter to be as effective as the former to bind halogens.
-

Hydroxy Compounds (Digital Notes)
$50.00 Add to cartA hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom and having the chemical formula OH. Compounds such as alcohols, phenols, and carboxylic acids contain these groups.
-
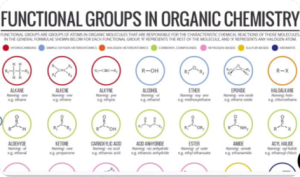
Introduction to Organic Chemistry (Stereoisomerism)
Read more -
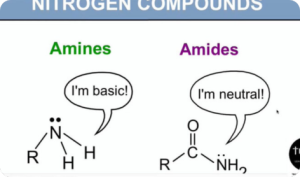
Nitrogen Compounds (Digital Notes)
$150.00 Add to cartNitrogen compounds such as urea, amine and guanidine are used to denature proteins, hence their antimicrobial properties. One special form of nitrogen compounds for antimicrobial treatment is the so-called quats or quaternary ammonium salts. These molecules have a positive charge, attracting the negatively charged cell membrane of microorganisms.
-

Reaction Kinetics (Digital Notes)
$250.00 Add to cartChemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is to be contrasted with chemical thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in which a reaction occurs but in itself tells nothing about its rate. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how experimental conditions influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction’s mechanism and transition states, as well as the construction of mathematical models that also can describe the characteristics of a chemical reaction.