Showing 7–12 of 17 results
-
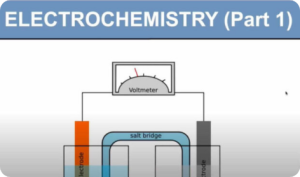
Electrochemical Cell (Digital Notes)
$150.00 Add to cartAn electrochemical cell is a device that can generate electrical energy from the chemical reactions occurring in it, or use the electrical energy supplied to it to facilitate chemical reactions in it.
-
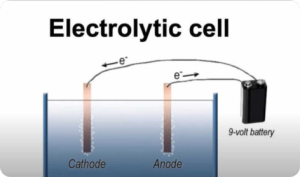
Electrolysis (Digital Notes)
Read moreElectrolysis is a process that involves the use of an electric current to drive a chemical reaction. It is a fundamental process in chemistry and is used in a wide range of applications, including the production of metals, the purification of chemicals, and the generation of electricity.
-
Gibbs Free Energy (Digital Notes)
Read moreGibbs free energy, denoted G, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. The change in free energy, ΔG, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system. ΔG can predict the direction of the chemical reaction under two conditions: 1. constant temperature and 2. constant pressure.
-
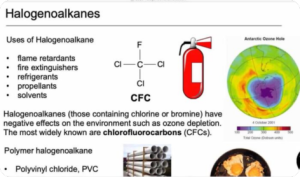
Halogen Derivatives (Digital Notes)
$150.00 Add to cartThe term “halogen derivatives” refer to the organic compounds of halogens which usually contain covalently-bonded halogens. The electronegativity of elements plays a crucial role in deciding which get to bond with halogens and which don’t. The similarity in electronegativity values of H and C render the latter to be as effective as the former to bind halogens.
-

Hydroxy Compounds (Digital Notes)
$50.00 Add to cartA hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom and having the chemical formula OH. Compounds such as alcohols, phenols, and carboxylic acids contain these groups.
-
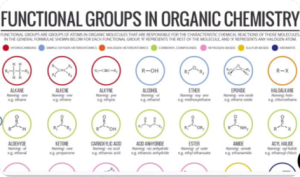
Introduction to Organic Chemistry (Stereoisomerism)
Read more