Description
Course Content
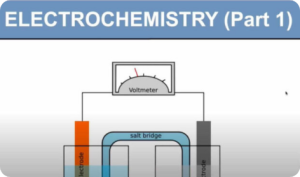
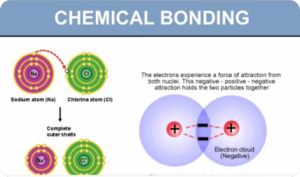
- Redox processes: electron transfer and changes in oxidation number (oxidation state)
- Relative masses of atoms and molecules
- The mole, the Avogadro constant
- The calculation of empirical and molecular formulae
- Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases)
Learning Outcomes
- the term relative formula mass or M r will be used for ionic compounds
Candidates should be able to:
- (a) define the terms relative atomic, isotopic, molecular and formula mass
- (b) define the term mole in terms of the Avogadro constant
- (c) calculate the relative atomic mass of an element given the relative abundances of its isotopes
- (d) define the terms empirical and molecular formula
- (e) calculate empirical and molecular formulae using combustion data or composition by mass
- (f) write and/or construct balanced equations
- (g) perform calculations, including use of the mole concept, involving:
- (i) reacting masses (from formulae and equations)
- (ii) volumes of gases (e.g. in the burning of hydrocarbons)
- (iii) volumes and concentrations of solutions
(when performing calculations, candidates’ answers should reflect the number of significant figures given or asked for in the question) - (h) deduce stoichiometric relationships from calculations such as those in (g)