Chem On Demand
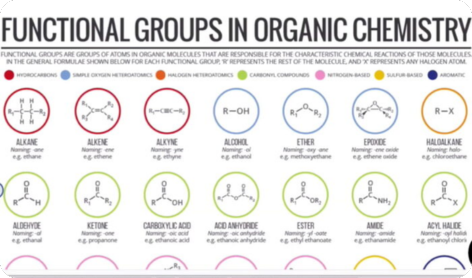
Introduction to Organic Chemistry (Stereoisomerism)
Related products
-
Gibbs Free Energy (Digital Notes)
Read moreGibbs free energy, denoted G, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. The change in free energy, ΔG, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system. ΔG can predict the direction of the chemical reaction under two conditions: 1. constant temperature and 2. constant pressure.
-
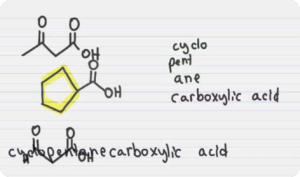
Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives (Digital Notes)
$200.00 Add to cartCarboxylic Acid is an organic compound containing a carboxyl functional group. They occur widely in nature and are also synthetically manufactured by humans. Upon deprotonation, carboxylic acids yield a carboxylate anion with the general formula R-COO–, which can form a variety of useful salts such as soaps.
-

Hydroxy Compounds (Digital Notes)
$50.00 Add to cartA hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom and having the chemical formula OH. Compounds such as alcohols, phenols, and carboxylic acids contain these groups.
-

Alkanes (Digital Notes)
Read moreAlkanes are organic compounds that consist of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms. The formula for Alkanes is CnH2n+2, subdivided into three groups – chain alkanes, cycloalkanes, and the branched alkanes.